Gastritis: Causes, Symptoms & Expert Treatment by Specialists
That familiar burning sensation in your stomach after a spicy meal, the uncomfortable bloating that ruins your afternoon, or the persistent indigestion that has become your unwelcome companion. For many in India, these aren't just occasional discomforts; they are daily realities. This condition, known as gastritis, is an inflammation of the stomach lining. While it might sound simple, its impact on daily life can be significant. From our rich, flavourful cuisine to the fast-paced, high-stress lifestyles many of us lead, the triggers for gastritis are woven into the fabric of our culture. It's a widespread issue, yet often misunderstood and self-treated with temporary remedies.
However, distinguishing between a simple stomach upset and a more persistent problem like chronic gastritis requires professional insight. This is where consulting a Gastroenterologist becomes not just a choice, but a necessity for accurate diagnosis and effective, long-term relief. This blog aims to be your comprehensive guide, answering the most common questions patients have about this condition. We'll delve into its causes, symptoms, and the advanced treatments available, drawing upon expert knowledge to provide clarity and direction. Think of this as a direct conversation with a specialist, designed to empower you with the information you need to take control of your digestive health, with insights informed by leading institutions like Bangalore Gastro Centre.
Understanding Gastritis
Q: What exactly is gastritis?
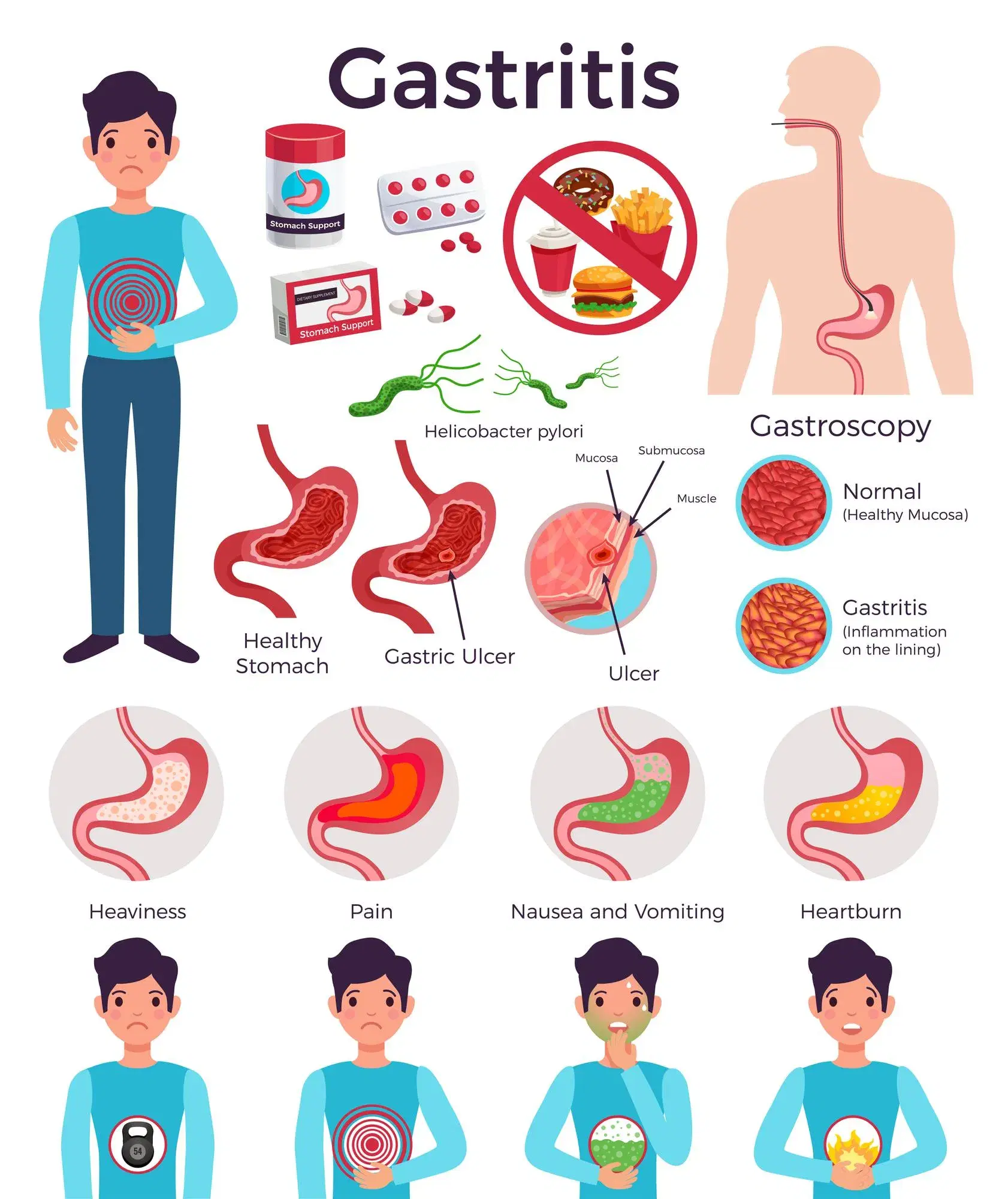
At its core, gastritis is the inflammation, irritation, or erosion of the lining of the stomach, known as the mucosa. Imagine the stomach lining as a protective barrier, similar to the inner tube of a tire. When this barrier is weakened or damaged, the powerful digestive acids produced by the stomach can directly attack the lining, causing inflammation and pain. This is the fundamental mechanism of gastritis.
It's not a single disease but rather a condition that can manifest in different ways, primarily categorized into two main types:
- Acute Gastritis: This form appears suddenly and is often characterized by sharp, severe symptoms. The onset can be abrupt, perhaps after taking certain medications, consuming excessive alcohol, or experiencing a significant physical stressor like a major surgery or injury. The inflammation is intense but typically short-lived if the underlying cause is removed.
- Chronic Gastritis: This is a more insidious form of the condition. It develops gradually over a long period, and the symptoms might be duller or less noticeable than in the acute form. Sometimes, individuals with chronic gastritis may not experience any symptoms for years until the inflammation leads to more significant complications like an ulcer or anemia. It can be caused by long-term infections, persistent irritation from substances, or autoimmune responses.
Understanding the distinction between these two is vital. While acute gastritis might resolve relatively quickly with treatment, untreated chronic gastritis can lead to a gradual wearing away of the stomach lining (atrophic gastritis), increasing the risk of more severe health issues. Early detection is crucial because it allows for timely intervention to heal the stomach lining and prevent this progression. A Gastroenterologist is trained to perform the necessary diagnostic tests to differentiate between these types and identify the root cause, ensuring that the treatment plan is not just about managing symptoms but about addressing the core problem for lasting health.
Causes of Gastritis (Prominent Q&A)
Q: What causes gastritis?
This is perhaps the most critical question patients ask, as understanding the "why" is the first step toward effective treatment and prevention. Gastritis isn't caused by a single factor; rather, it's the result of various triggers that compromise the stomach's protective lining. A Gastroenterologist will meticulously investigate your history to pinpoint the specific cause. Let's explore the most common culprits in detail:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection: This is the leading cause of gastritis worldwide. H. pylori is a type of bacteria that can colonize the stomach lining. It's incredibly resilient and can survive in the highly acidic environment of the stomach. The bacteria work by weakening the protective mucous layer, making the stomach lining vulnerable to damage from digestive acids. This infection is often acquired in childhood and can persist for life if not treated. It is a primary driver of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and, in some cases, stomach cancer.
- Regular Use of Painkillers (NSAIDs): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are common over-the-counter medications used for pain and inflammation, including ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. While effective for pain relief, their regular or excessive use can be detrimental to the stomach. These drugs inhibit the production of substances called prostaglandins, which play a crucial role in protecting the stomach lining from acid. This disruption can lead to both acute and chronic forms of gastritis.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption and Smoking: Both alcohol and tobacco are significant irritants to the stomach mucosa. Alcohol can directly irritate and erode the stomach lining, leading to increased acid production and inflammation. Similarly, smoking impairs blood flow to the stomach, hinders the production of protective mucus, and can increase the risk of H. pylori infection, creating a perfect storm for gastritis to develop.
- Stress and Autoimmune Conditions: Severe physiological stress—from major surgery, traumatic injury, or critical illness—can cause a sudden onset of acute gastritis, often called stress gastritis. This is due to reduced blood flow to the stomach. Furthermore, psychological stress, while not a direct cause, can exacerbate symptoms by increasing stomach acid production. In some cases, the body's own immune system can mistakenly attack the cells of the stomach lining. This is known as autoimmune gastritis, a form of chronic gastritis that can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency and pernicious anemia.
- Bile Reflux: Bile is a digestive fluid produced in the liver and is essential for digesting fats. Normally, it flows from the liver to the small intestine. However, if the pyloric valve (which separates the stomach from the small intestine) doesn't function correctly, bile can flow backward into the stomach. This backwash, known as bile reflux, irritates the stomach lining and can cause gastritis.
Can chronic gastritis develop if causes are left untreated?
Absolutely. This is a critical point to understand. When the triggers mentioned above are not identified and managed, the stomach lining is subjected to continuous inflammation. This persistent state is the definition of chronic gastritis. Over time, this ongoing damage can lead to serious complications, including:
- Peptic Ulcers: Open sores that develop on the stomach lining.
- Atrophic Gastritis: A thinning of the stomach lining, which impairs digestion.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Particularly vitamin B12, leading to pernicious anemia.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term, untreated gastritis, especially when caused by H. pylori, is a known risk factor for developing stomach cancer.
This is precisely why identifying the root cause with the help of a Gastroenterologist is not just important—it's essential for your long-term health. A specialist can conduct the right tests to determine if H. pylori, NSAIDs, or another factor is the culprit and create a targeted treatment plan.
Recognizing Symptoms of Gastritis
Q: How do I know if I might have gastritis?
The symptoms of gastritis can range from mildly annoying to severely debilitating, and they often overlap with other digestive issues like indigestion or acid reflux. This can make self-diagnosis tricky and unreliable. However, there are several key signs that should prompt you to consider the possibility of gastritis and seek a professional opinion.
The most common symptoms include:
- Burning or Gnawing Pain in the Upper Abdomen: This is the hallmark symptom. The pain, often described as a burning sensation, is typically felt in the upper central part of the stomach (the epigastrium). It can either improve or worsen after eating, depending on the individual and the cause.
- Nausea and Vomiting: The inflammation can disrupt the normal digestive process, leading to feelings of nausea. In some cases, this can progress to vomiting. The vomit may be clear, green, or yellow (containing bile), or, in severe cases, contain blood.
- Bloating and a Feeling of Fullness: Many people with gastritis report feeling uncomfortably full, especially in the upper abdomen, even after eating a small amount of food. This is often accompanied by bloating and belching.
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia): This is a general term for a persistent or recurrent pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen. It's a very common symptom of gastritis.
While these are the most prominent signs, chronic gastritis can present with more subtle and systemic symptoms due to its long-term nature. These can include:
- Loss of Appetite: The constant discomfort can naturally lead to a decreased desire to eat.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A consequence of a poor appetite and impaired nutrient absorption.
- Fatigue and Weakness: If chronic gastritis leads to vitamin B12 deficiency or slow, chronic bleeding from the stomach lining, it can cause anemia. This results in persistent tiredness, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
When should I see a Gastroenterologist?
It's advisable to consult a doctor if you experience any of these symptoms for more than a week, or if they are severe. You should see a Gastroenterologist promptly if your symptoms are accompanied by dizziness, weakness, or if you notice blood in your vomit or stool. While a single episode of indigestion might not be a cause for alarm, persistent or recurring symptoms are your body's way of signaling that something is wrong with your stomach's health and requires a thorough investigation.
Diagnosis by a Gastroenterologist
Q: How do doctors diagnose gastritis?
Diagnosing gastritis accurately is a multi-step process that goes beyond just listening to your symptoms. A Gastroenterologist will use a combination of methods to confirm the presence of inflammation, identify its underlying cause, and determine whether it is acute or chronic. This systematic approach ensures that the treatment is precise and effective.
Here are the common diagnostic methods you can expect:
- Physical Examination and Medical History: The consultation will always begin with a detailed conversation. The specialist will ask about your symptoms, their duration and severity, your diet, lifestyle habits (like alcohol and smoking), and any medications you are taking, especially NSAIDs. A physical exam, where the doctor gently presses on your abdomen to check for tenderness, will also be performed.
- Upper GI Endoscopy (Gastroscopy): This is the most definitive test for diagnosing gastritis. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera on the end (an endoscope) is passed down your throat into your esophagus, stomach, and the first part of your small intestine. This allows the specialist to directly visualize the stomach lining and look for signs of inflammation, redness, erosions, or ulcers.
- Biopsy: If the specialist observes suspicious areas during the endoscopy, they can take a small tissue sample (a biopsy) from the stomach lining. This tissue is then sent to a lab to be examined under a microscope. A biopsy can confirm the presence of gastritis, check for the H. pylori bacteria, and rule out other more serious conditions.
- Tests for H. pylori: Since H. pylori is a primary cause, specific tests are often conducted. These include:
- Blood Test: To check for antibodies to the bacteria.
- Stool Test: To detect H. pylori antigens in your stool.
- Urea Breath Test: A non-invasive test where you drink a special liquid and then breathe into a bag. The test measures carbon dioxide levels, which are higher if H. pylori is present.
A Gastroenterologist uses these tools not just to say "you have gastritis," but to answer critical follow-up questions: Is it acute or chronic? Is H. pylori the cause? Is there any pre-cancerous change? This detailed diagnosis is the foundation of a successful treatment strategy.
Treatment Options Explained
Q: How is gastritis treated by specialists?
The treatment for gastritis is not a one-size-fits-all solution. A Gastroenterologist tailors the approach based on the specific cause, severity, and type (acute or chronic) of your condition. The goal is twofold: to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach to relieve symptoms and allow the lining to heal, and to treat the underlying cause to prevent recurrence.
The treatment plan typically involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes:
1. Medication:
- Antacids: Over-the-counter medications like Digene or Gelusil can provide quick, temporary relief by neutralizing stomach acid. However, they don't heal the underlying inflammation.
- Acid Blockers (H2 Blockers): Medications like ranitidine or famotidine work by reducing the amount of acid the stomach produces. They provide longer relief than antacids.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These are more powerful acid reducers and include drugs like omeprazole, pantoprazole, and esomeprazole. They work by blocking the action of the tiny "pumps" within the stomach's acid-secreting cells. PPIs are very effective at promoting the healing of the stomach lining.
- Antibiotics for H. pylori: If your gastritis is caused by an H. pylori infection, the specialist will prescribe a combination of antibiotics (often two or three different types) along with a PPI. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the bacteria are completely eradicated.
2. Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications:
Medication is only one part of the equation. Your specialist will also guide you on making important lifestyle changes to support healing and prevent flare-ups. This includes avoiding known irritants like alcohol, smoking, and spicy or fatty foods. We will discuss this in more detail in the next section on the gastritis diet plan.
"Can chronic gastritis be fully cured?"
This is a common and important question. The answer depends heavily on the cause. If chronic gastritis is caused by H. pylori or long-term NSAID use, it can often be effectively "cured" by eradicating the bacteria or stopping the offending medication. In these cases, the stomach lining has a remarkable ability to heal itself once the source of irritation is removed.
However, if the gastritis is due to an autoimmune condition or other persistent factors, it may not be fully curable but can be very effectively managed. The focus then shifts to long-term control of inflammation, management of symptoms, and prevention of complications. This requires a dedicated approach, including adherence to a gastritis diet plan and regular follow-ups with your Gastroenterologist. These check-ups are essential to monitor the condition of your stomach lining and adjust the treatment plan as needed, ensuring you maintain a good quality of life. For those dealing with related digestive issues, understanding your options is key. For instance, many find it helpful to read guides on Finding the Right IBS Specialist: A Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment in India to see how specialist care addresses different gut problems.
Role of Diet in Managing Gastritis
Q: What foods should I eat or avoid if I have gastritis?
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing gastritis. The food you eat can either soothe your inflamed stomach lining or aggravate it further. While there is no single "magic" diet for everyone, a well-structured gastritis diet plan, often created in consultation with your specialist or a dietitian, is a cornerstone of effective management. The primary goal of this diet is to minimize irritation and promote healing.
Foods That Soothe and Are Generally Well-Tolerated:
Think of these as "stomach-friendly" foods. They are typically low in acid, fat, and spice.
- Soft-Cooked Grains: White rice, khichdi (made with minimal spice), oats, and semolina (suji) are easy to digest.
- Lean Proteins: Boiled or steamed chicken and fish are good options. For vegetarians, well-cooked lentils (dal) and moong are excellent choices.
- Fruits: Low-acid fruits like bananas, papayas, melons, and apples (stewed or peeled) are generally safe.
- Vegetables: Most cooked vegetables are beneficial, especially potatoes, carrots, pumpkin, and leafy greens.
- Healthy Fluids: Coconut water is incredibly soothing and hydrating. Herbal teas like chamomile or ginger tea (in moderation) can also be beneficial.
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
These are common triggers that can increase stomach acid, cause irritation, and worsen symptoms.
- Spicy and Oily Foods: This includes curries with heavy masalas, fried items like samosas and pakoras, and pickles.
- Acidic Foods: Tomatoes, citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), and their juices can be highly irritating.
- Processed and Fatty Foods: Packaged snacks, red meat, and full-fat dairy products can delay stomach emptying and increase discomfort.
- Caffeinated and Carbonated Drinks: Coffee, strong tea, sodas, and other fizzy drinks can increase stomach acid and cause bloating.
- Alcohol: As a major irritant, alcohol should be avoided completely during a flare-up and limited significantly in the long term.
Does diet help chronic gastritis patients?
Yes, immensely. For individuals with chronic gastritis, a carefully managed gastritis diet plan is not just about avoiding triggers during a flare-up; it's a long-term strategy for healing and prevention. A consistent, stomach-friendly diet helps to reduce the daily burden on the stomach lining, giving it the best possible environment to heal. It minimizes the frequency and severity of flare-ups, reduces reliance on medication, and significantly improves overall quality of life.
For quick and practical tips on managing gastric discomfort at home, you can watch this helpful video: Gastric Problem Solved With These Home Remedies. It offers simple remedies that can complement your prescribed treatment plan.
Lifestyle Tips for Prevention and Healing
Q: Can lifestyle changes really make a difference?
Yes, they can make a profound difference. While medication and diet are crucial, your daily habits and routines play a significant supporting role in both healing from a gastritis episode and preventing future occurrences. Think of these changes as creating a healthier environment for your stomach to function optimally.
Here are some impactful lifestyle adjustments:
- Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Instead of three large meals, try eating five or six smaller meals throughout the day. This prevents the stomach from being overloaded and reduces the amount of acid released at any one time.
- Reduce Stress: There is a strong connection between the mind and the gut. High levels of stress can trigger an increase in stomach acid production. Incorporating stress-management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or even a simple daily walk can be incredibly beneficial.
- Avoid Late-Night Eating: Give your stomach at least 2-3 hours to digest before you lie down to sleep. Eating a heavy meal and then immediately going to bed can lead to acid reflux and increased irritation overnight.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: As discussed earlier, both are major irritants. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are two of the most effective lifestyle changes you can make for your stomach health.
- Chew Your Food Thoroughly: Digestion begins in the mouth. Chewing your food well breaks it down into smaller particles, making it easier for your stomach to process.
These changes work in synergy with your medical treatment to reduce the risk factors associated with chronic gastritis and support the healing process.
When to Seek Immediate Specialist Help
Q: What are the warning signs that I need urgent medical care?
While most cases of gastritis can be managed with a planned visit to a specialist, certain symptoms are red flags that indicate a potentially severe or complicated issue. These symptoms should not be ignored and require immediate medical attention.
Seek urgent care from a Gastroenterologist or at the nearest hospital if you experience any of the following:
- Vomiting Blood or Material that Looks Like Coffee Grounds: This is a sign of significant bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Black, Tarry Stools: This indicates digested blood in your stool, another sign of internal bleeding.
- Severe, Unrelenting Abdominal Pain: Pain that is sharp, constant, and doesn't ease with simple remedies could signal a complication like a perforation or a deep ulcer.
- Rapid, Unexplained Weight Loss: While some weight loss can occur with poor appetite, a significant and rapid drop in weight needs urgent investigation.
- Feeling Dizzy, Faint, or Extremely Weak: These can be symptoms of anemia caused by chronic blood loss.
These warning signs can point to serious complications of gastritis, such as a bleeding ulcer. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent severe health consequences. Do not delay seeking help if you experience any of these symptoms.
Expert Insights from Specialists
Q: What do gastroenterologist recommend for long-term management?
When you consult a gastroenterologist, their goal extends beyond just treating your immediate symptoms. They focus on creating a sustainable plan for long-term digestive health, especially for patients dealing with chronic gastritis. The advice is holistic, combining medical treatment with practical, everyday strategies.
Here is a summary of typical specialist recommendations for long-term management:
- Adherence to Prescribed Treatment: The most important advice is to stick to your treatment plan. This means taking your medications as prescribed, especially completing the full course of antibiotics for H. pylori, to prevent the infection from returning.
- Commitment to a Gastritis Diet Plan: Specialists emphasize that diet is not a temporary fix but a long-term commitment. Consistently avoiding your personal trigger foods and focusing on a balanced, non-irritating diet is key to keeping inflammation at bay.
- Regular Check-ups and Monitoring: For chronic gastritis, regular follow-up appointments are essential. These visits allow the specialist to monitor your progress, assess the health of your stomach lining (sometimes with a repeat endoscopy), and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment.
- Informed Medication Use: Always discuss any new medications, including over-the-counter painkillers, with your specialist. They can advise on safer alternatives if you need pain relief.
Specialized centers like Bangalore Gastro Centre are equipped to provide this kind of comprehensive, long-term care. Their focus on holistic management ensures that patients receive not just medical treatment, but also the education and support needed to manage their condition effectively for years to come.
Myths and Misconceptions about Gastritis
Q: Are common beliefs about gastritis true?
Gastritis is so common that numerous myths and home-remedy beliefs have sprung up around it. While some may have a grain of truth, many are misleading and can prevent people from seeking proper medical care. A Gastroenterologist can help you separate fact from fiction.
Let's bust some common myths:
- Myth 1: "Drinking cold milk cures gastritis instantly."
- Fact: While cold milk might provide a temporary soothing sensation by coating the stomach and neutralizing acid, this effect is short-lived. The fat and protein in milk can later stimulate the stomach to produce more acid, potentially making symptoms worse in the long run.
- Myth 2: "Spicy food is the only cause of gastritis."
- Fact: While spicy food can certainly aggravate existing gastritis or trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals, it is rarely the sole underlying cause. As we've discussed, the most common causes are H. pylori infection and NSAID use. Blaming only spicy food oversimplifies the issue.
- Myth 3: "Home remedies are enough to cure gastritis."
- Fact: Certain home remedies, like ajwain (carom seeds) or ginger tea, can help manage mild symptoms of indigestion. However, they cannot cure the underlying inflammation or eradicate an H. pylori infection. Relying solely on home remedies for a persistent problem can delay proper diagnosis and treatment, allowing the condition to worsen.
These myths highlight why seeking balanced, evidence-based advice from a qualified Gastroenterologist is so important. They can provide a scientifically sound diagnosis and treatment plan that addresses the root cause of your problem.
Living with Chronic Gastritis
Q: How do patients cope with chronic gastritis daily?
Living with a chronic condition like gastritis is about more than just managing physical symptoms; it involves emotional and lifestyle adjustments as well. The unpredictability of flare-ups can cause anxiety and frustration, impacting social life and daily routines. However, with the right approach and support, individuals can lead full and active lives.
Coping effectively involves several key aspects:
- Embracing the Gastritis Diet Plan: This is often the biggest daily adjustment. It requires mindful eating, planning meals in advance, and learning to navigate social situations like eating out or attending parties. It becomes a lifestyle rather than a restrictive diet over time.
- Building a Strong Support System: The journey is easier with support. Family members who understand the dietary needs, friends who are accommodating of meal choices, and a good relationship with your doctor and dietitian are invaluable. Open communication about your condition can reduce stress and make you feel less isolated.
- Listening to Your Body: Patients learn to recognize their personal triggers and the subtle early signs of a flare-up. This allows them to take proactive steps, like adjusting their diet or managing stress, to prevent the symptoms from escalating.
- Focusing on Mental Well-being: The gut-brain axis is a powerful connection. The stress of managing a chronic illness can worsen symptoms, creating a vicious cycle. Prioritizing mental health through relaxation techniques, hobbies, and, if needed, professional counseling is a crucial part of the coping strategy.
Living with chronic gastritis is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires patience, discipline, and a positive mindset, all guided by the expert care of a dedicated medical team.
To Conclude
Gastritis, in its many forms, is a condition that affects millions of people in India. From the sudden, sharp pain of acute gastritis to the persistent, nagging discomfort of its chronic counterpart, the impact on one's quality of life is undeniable. We've journeyed through the critical questions: understanding what it is, identifying its diverse causes like H. pylori and NSAID use, recognizing its tell-tale symptoms, and exploring the effective treatments available. We've also seen how a disciplined gastritis diet plan and positive lifestyle changes are not just recommendations but powerful tools for healing and long-term management.
The key takeaway from this comprehensive discussion is the indispensable role of professional medical guidance. Self-diagnosis and reliance on temporary fixes can mask underlying issues and lead to more severe complications. Consulting a Gastroenterologist is the most crucial step you can take towards recovery. They provide an accurate diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan, and the long-term support needed to navigate this condition successfully. By adopting healthier habits and seeking expert care, you can move beyond simply managing symptoms to achieving lasting digestive wellness.
For more trusted health insights and educational resources, we encourage you to subscribe to our YouTube channel and explore the information provided by expert centers like Bangalore Gastro Centre.
